Suspected case of Monkeypox detected in Nepal
Know what is monkeypox, its symptoms and how do you catch it
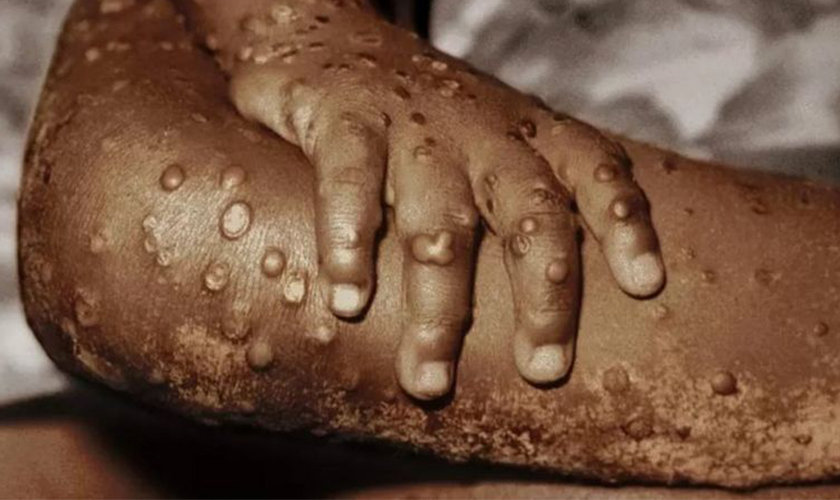
KATHMANDU, June 16: Suspected cases of monkeypox have been detected in Nepal.
A case similar to monkeypox was detected in a Nepali youth traveling from the United Arab Emirates (UAE). He is currently under medical supervision at Teku-based Sukraraj Tropical and Infectious Disease Hospital.
The youth, 27, had experienced 104 degrees of fever and rashes on his hands.
So far his health is normal, according to the Hospital.
How common is monkeypox?
Monkeypox is caused by the monkeypox virus, a member of the same family of viruses as smallpox, although it is much less severe and experts say chances of infection are low.
It occurs mostly in remote parts of central and west African countries, near tropical rainforests.
There are two main strains of virus - west Africa and central African - and it's the milder one from west Africa which is now circulating in other regions of the world.
The unusually high numbers of people infected with monkeypox outside of Africa with no travel links to the region, means the virus is now spreading in the community.
It is also advising those infected not to have sex while they have symptoms and use condoms for eight weeks after an infection, as a precaution.
What are the symptoms?
Initial symptoms include fever, headaches, swellings, back pain, aching muscles.
Once the fever breaks a rash can develop, often beginning on the face, then spreading to other parts of the body, most commonly the palms of the hands and soles of the feet.
The rash, which can be extremely itchy or painful, changes and goes through different stages before finally forming a scab, which later falls off. The lesions can cause scarring.
The infection usually clears up on its own and lasts between 14 and 21 days.
How do you catch it?
Monkeypox can be spread when someone is in close contact with an infected person. The virus can enter the body through broken skin, the respiratory tract or through the eyes, nose or mouth.
It has not previously been described as a sexually transmitted infection, but it can be passed on by close contact.
New guidance is advising anyone with the virus to abstain from sex while they have symptoms.
While there is currently no available evidence that monkeypox can be spread in sexual fluids, people confirmed to have the virus are advised to use condoms for eight weeks after infection as a precaution.
It can also be spread by contact with infected animals such as monkeys, rats and squirrels, or by virus-contaminated objects, such as bedding and clothing.
How dangerous is it?
Most cases of the virus are mild, sometimes resembling chickenpox, and clear up on their own within a few weeks.
Monkeypox can sometimes be more severe, however, and has been reported to have caused deaths in west Africa.
How common are outbreaks?
The virus was first identified in a captive monkey and since 1970 there have been sporadic outbreaks reported across 10 African countries.
In 2003 there was an outbreak in the US, the first time it had been seen outside Africa. Patients caught the disease from close contact with prairie dogs that had been infected by small mammals imported into the country. A total of 81 cases were reported, but none resulted in deaths.
In 2017, Nigeria experienced the largest known outbreak. There were 172 suspected cases and 75% of victims were men between 21 and 40 years old.
What is the treatment?
Outbreaks can be controlled by infection prevention.
Vaccination against smallpox has been proven to be 85% effective in preventing monkeypox.
The UK has bought doses of the smallpox vaccine, but it is not clear how many jabs might be given.
Antiviral drugs may also help.










Leave Comment